This family divides into 4 subclasses. The Curve is - in all cases - a representation of the analemma. (see page 'Displaying the Equation of Time'). All, except Spider Dials, require a nodus or a point gnomon. They are the commonest and easiest-to-make equation-corrected sundials. The Equation of Time is usually combined together with the longitude correction.
FULL ANALEMMAS
(see also Noon Marks, below)
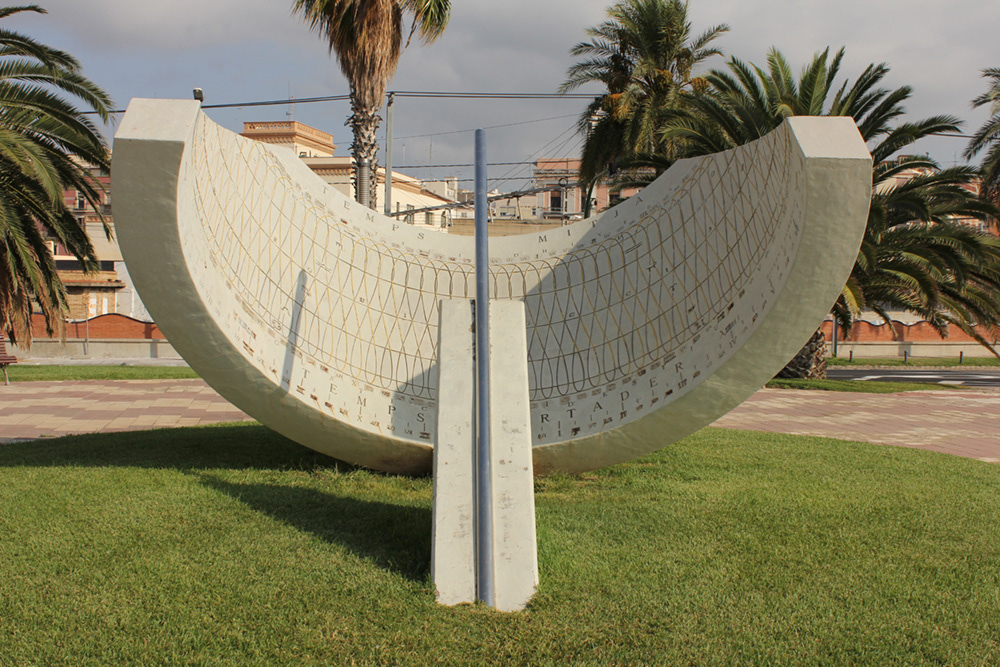

Rafel Soler i Gaya -1988 - Port of Tarragona, Catalonia
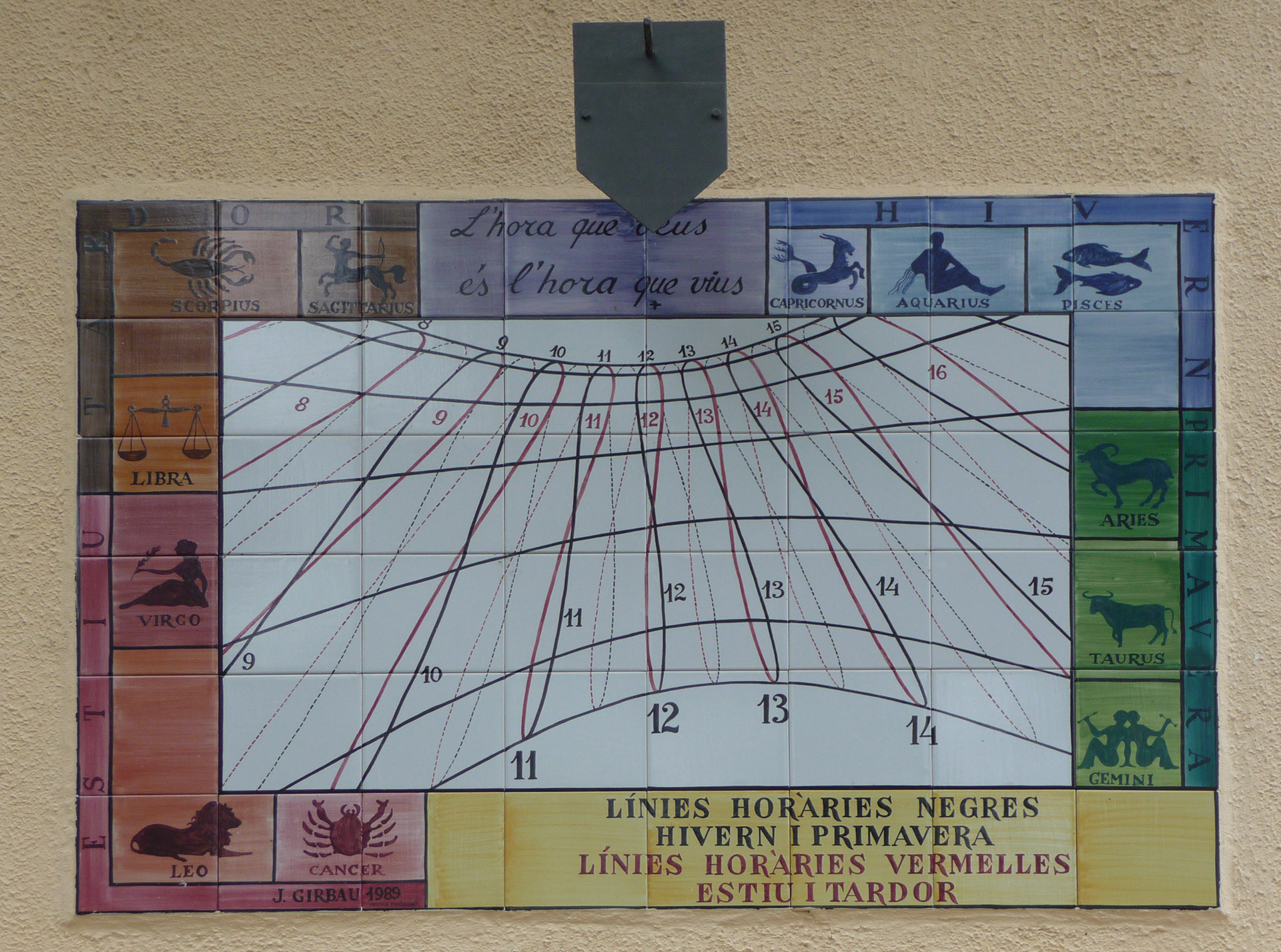
J Girbau - 1989 -Castelifollit de la Roca, Catalonia

Harriet James www.sunnydials.co.uk : East/West Vertical Declining Dial
Click on images to enlarge & view captions
HALF ANALEMMAS
These are easier to read than full analemmas, but either required the biannual change of the dial plate, as in the first two examples or two separate dials
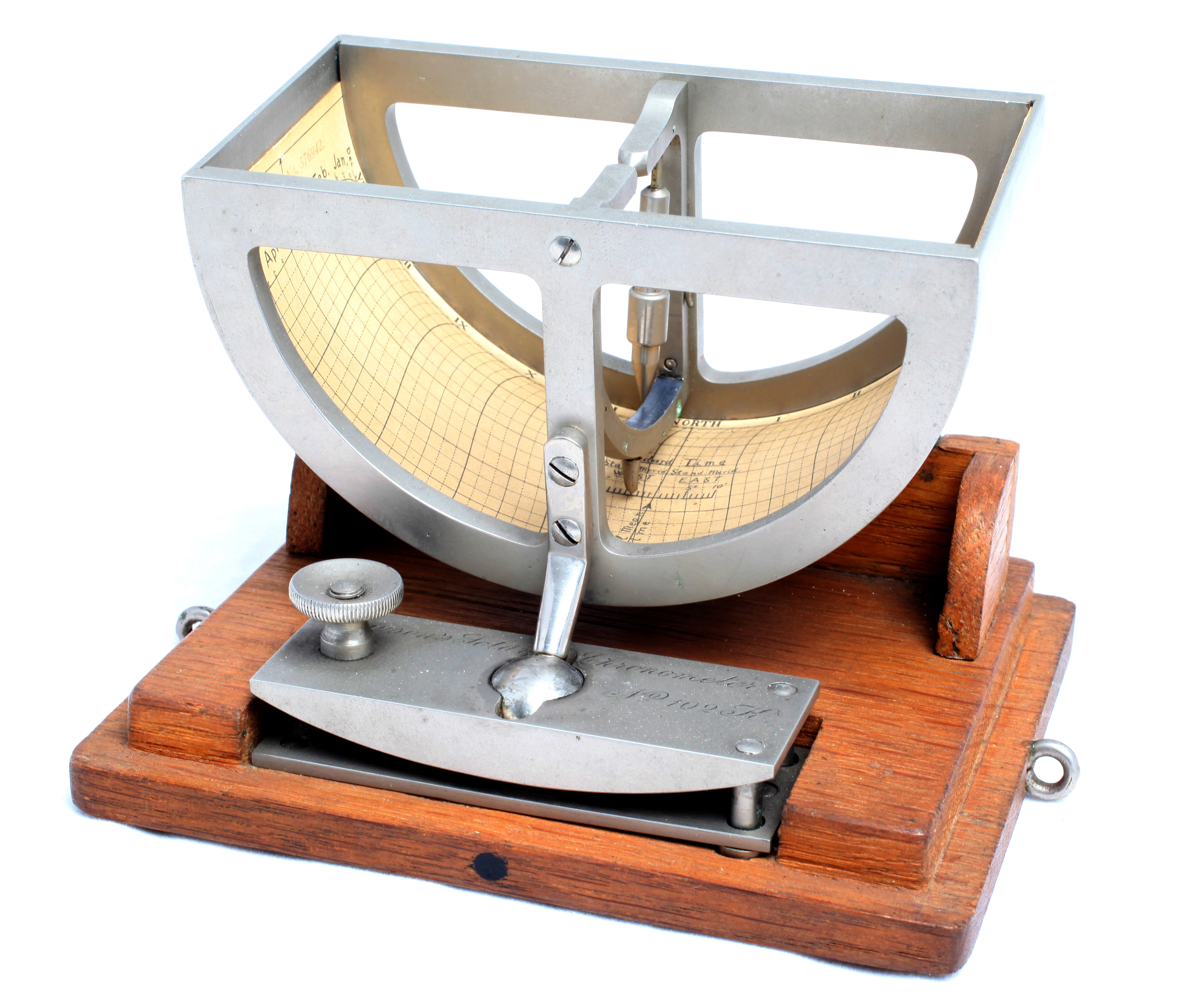

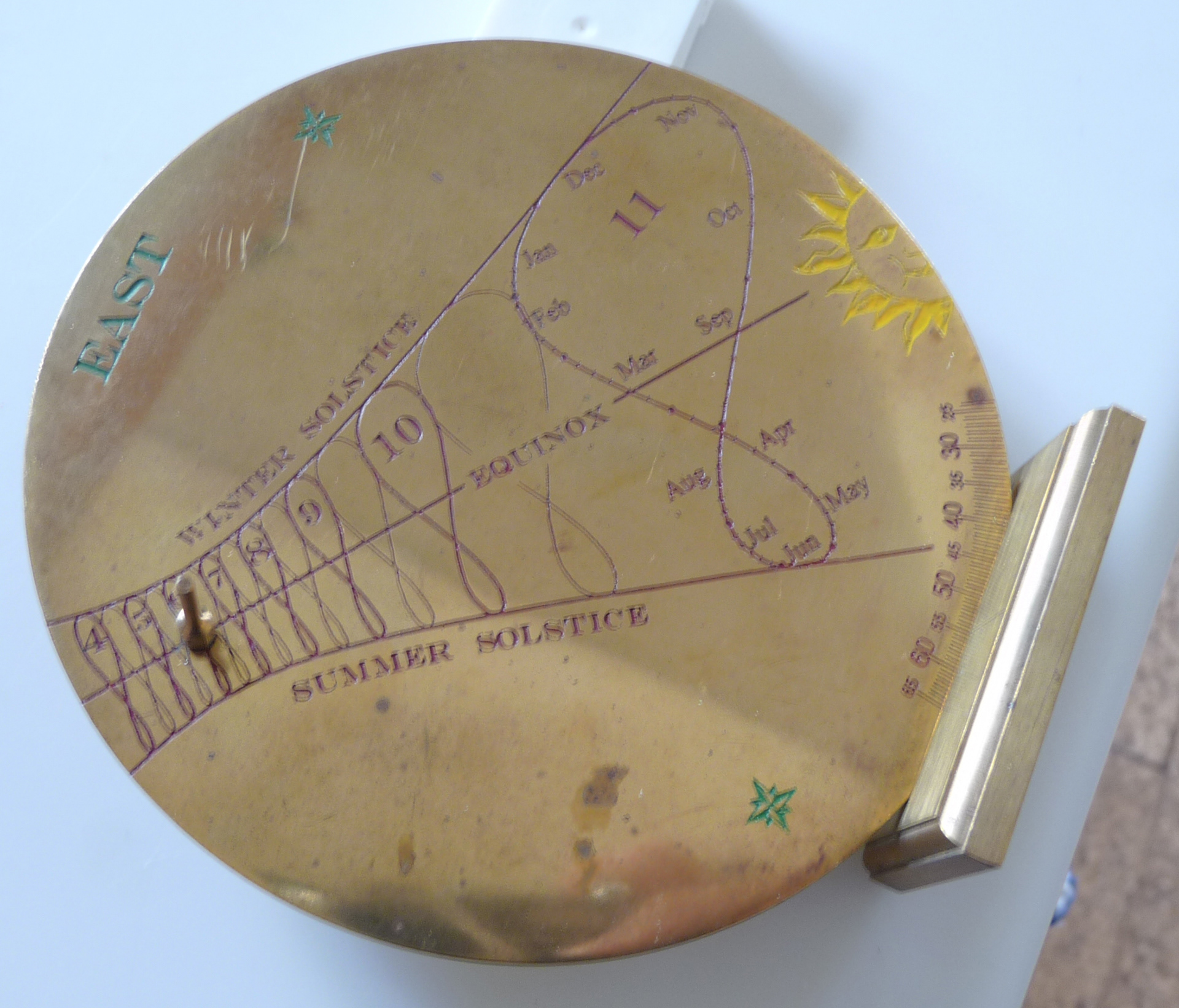
Ferguson Solar Chronometer - for use by Victorian travellers & explorers. Picture from Musée de la Vie Wallonne, Liège
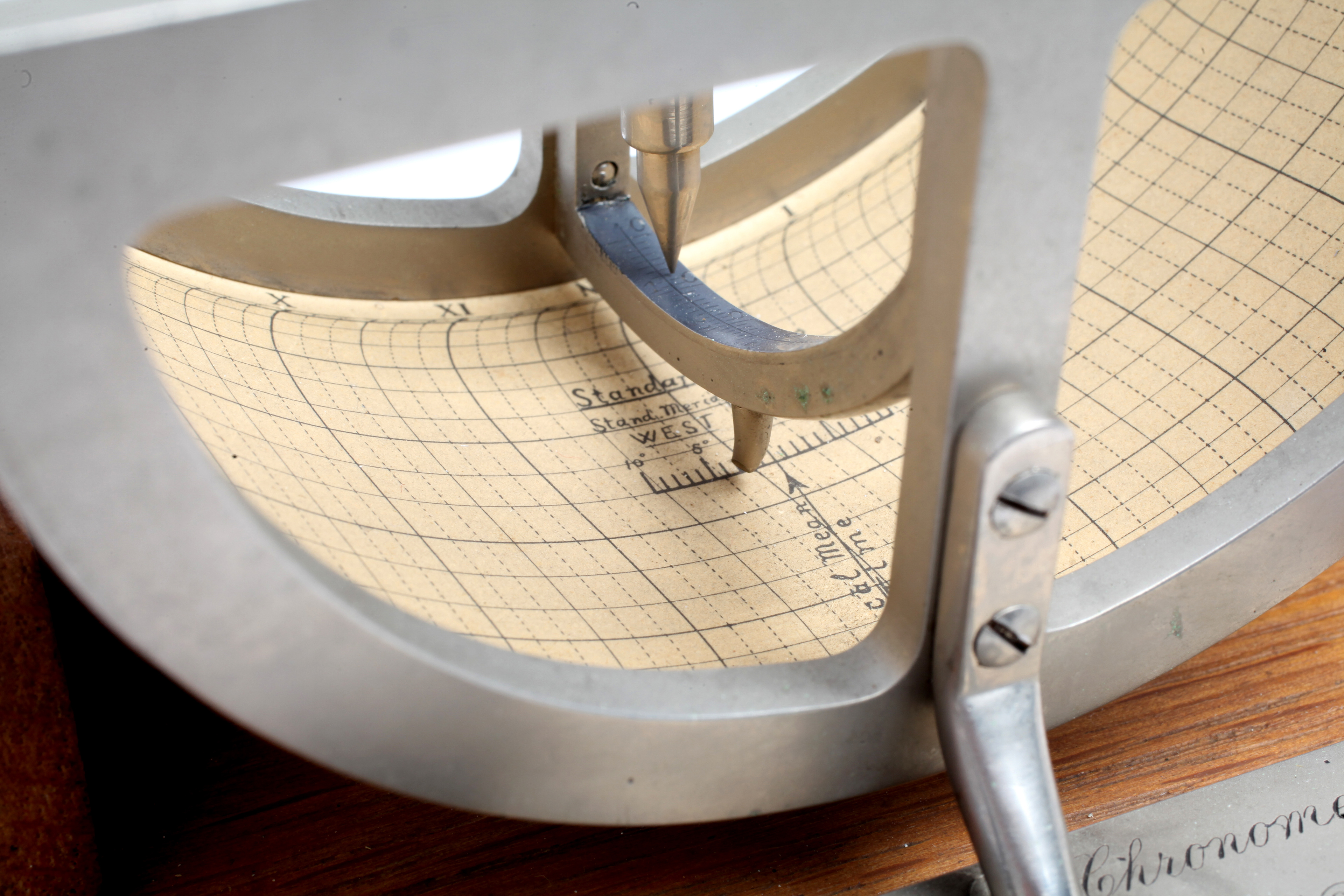

Detail from Ferguson Solar Chronometer
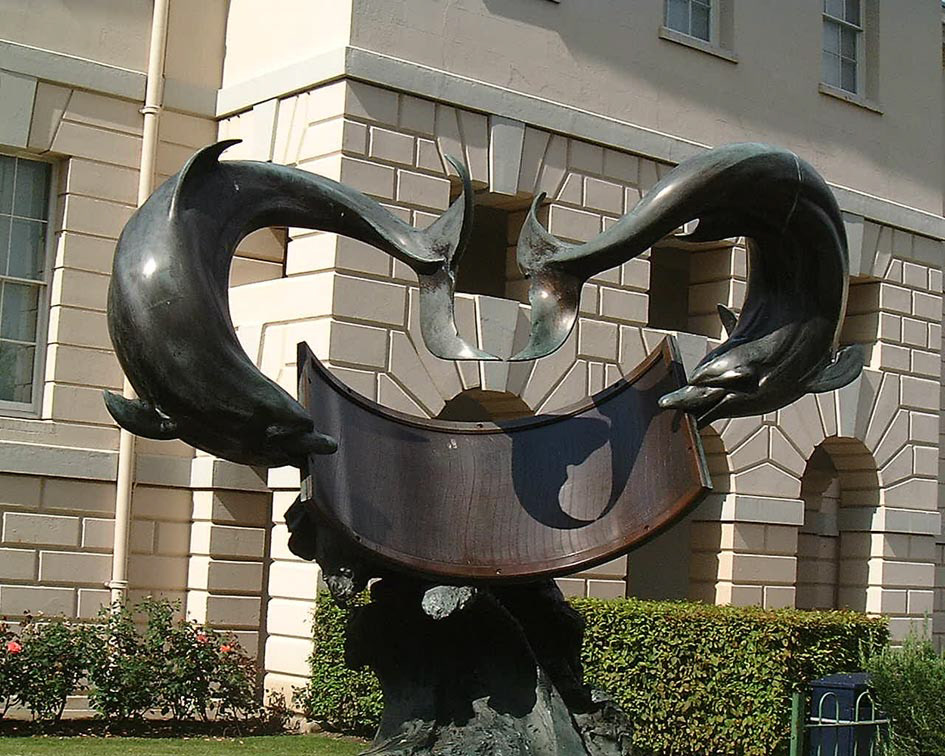

Christopher St. J. H. Daniel - 1977 - Dolphin Dial, Royal Observatory, London
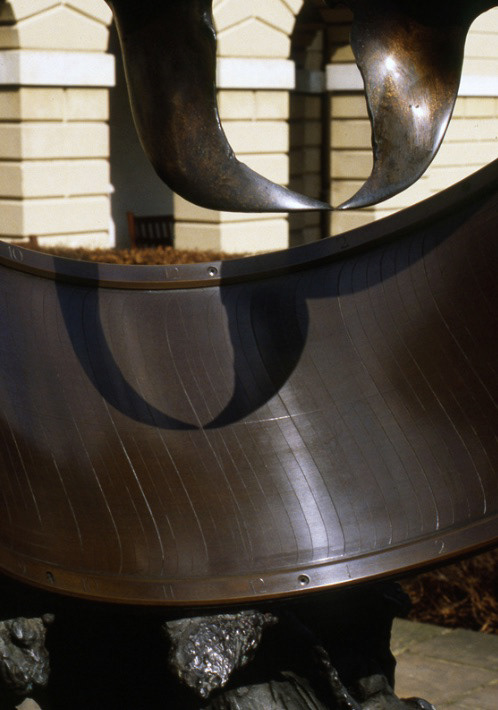

Detail from the Dolphin Dial
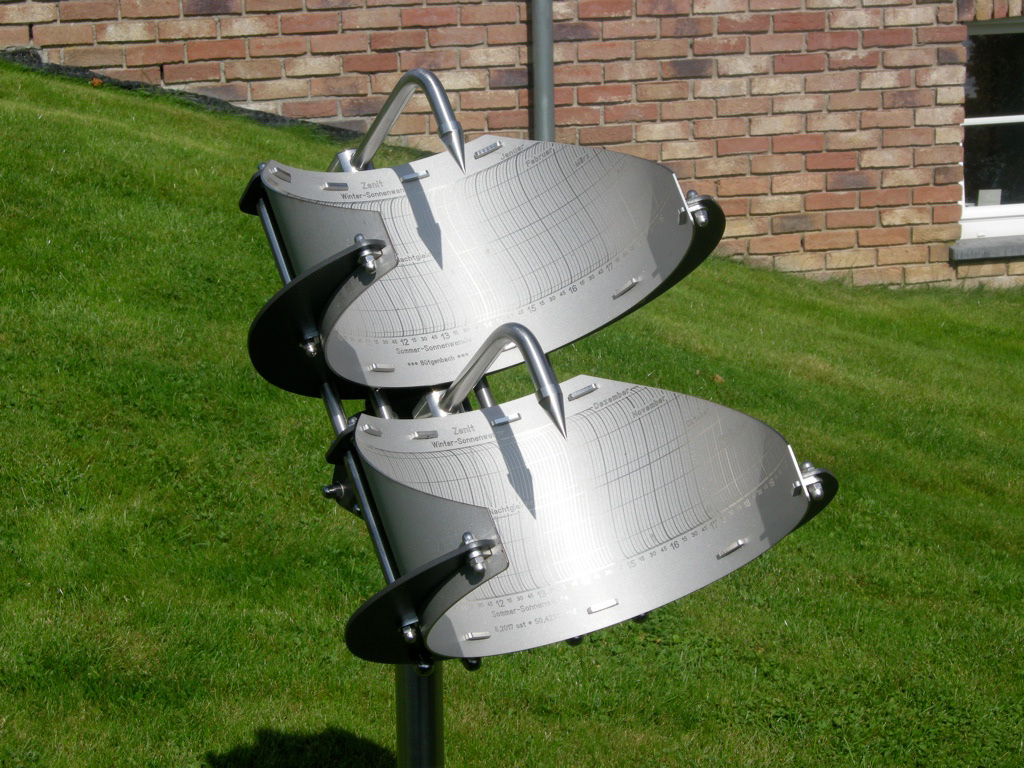

Albin Hoffmann - 2007 - www.precisionsundials.eu - Bütgenbach-Belgium
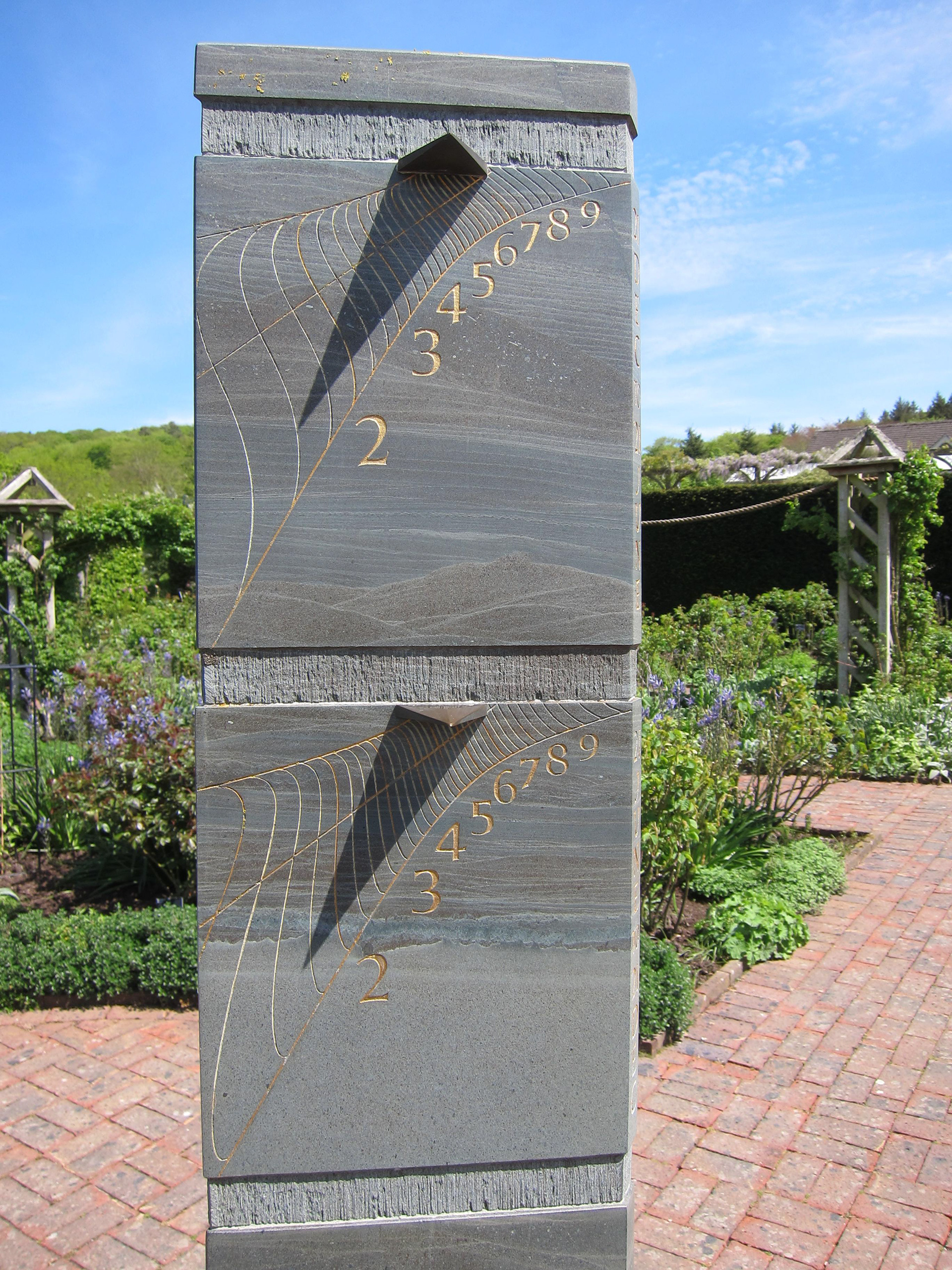

Sir Mark-Lennox Boyd & Ben Jones www.benjonessundials.co.uk - 2004 - Rosemoor Garden, Devon, UK

? Guiseppe Mara ? & ? Renaudi ? - 1997 -Chiusa di Pesio Nr Turin

W.F. Ng - 1986 - Magdalene College, Cambridge
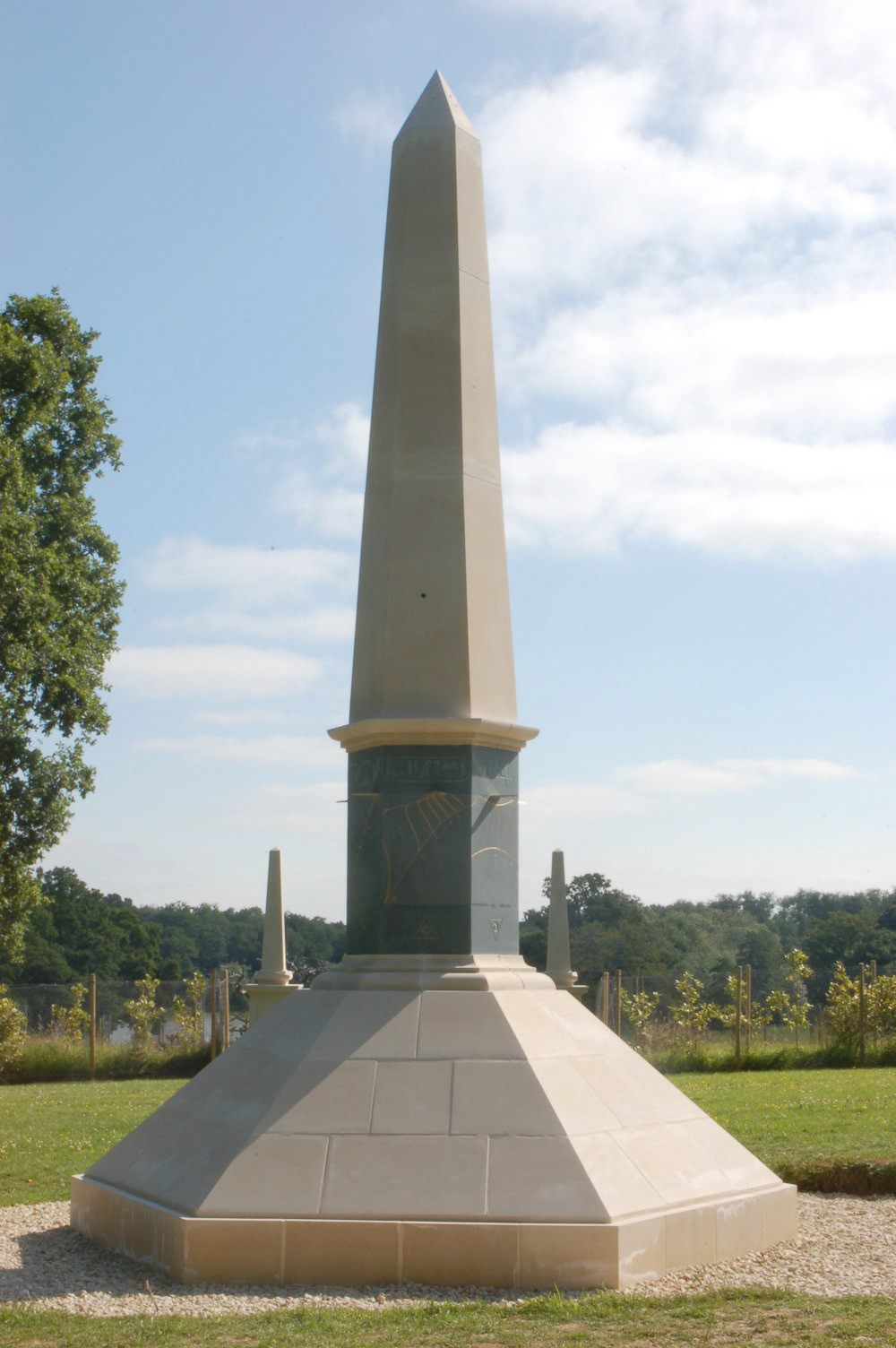

Sir Mark Lennon-Boyd & Fergus Wessel - 2013 - Obelisque Dial, Egyptian Garden, Buscot Park, Oxfordshire
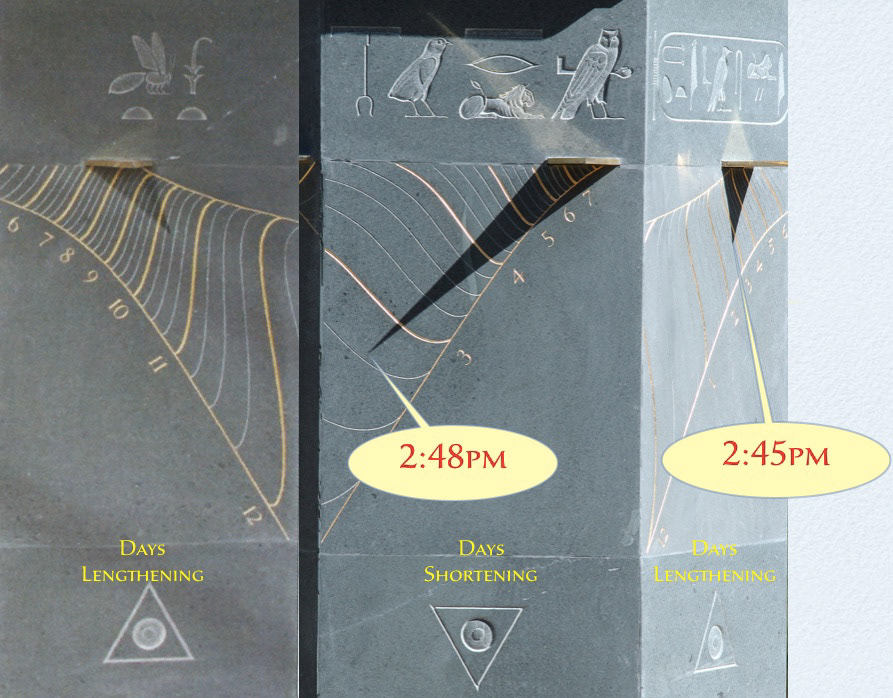
Detail from Obelisque Dial
Click on images to enlarge & view captions
NOON MARKS
These a subclass of the Full Analemma Class - but were often used to set church clocks.
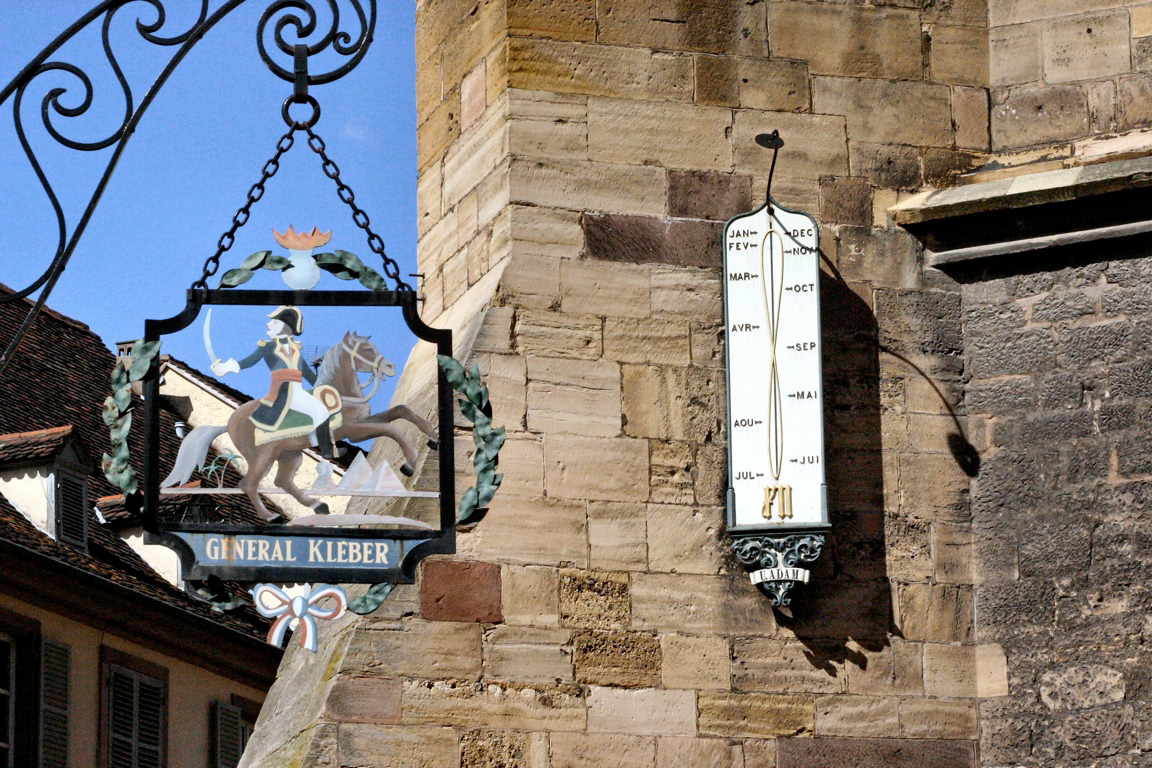

Urbain Adam - 1866 - Cathedral of St. Martin, Colmar, France
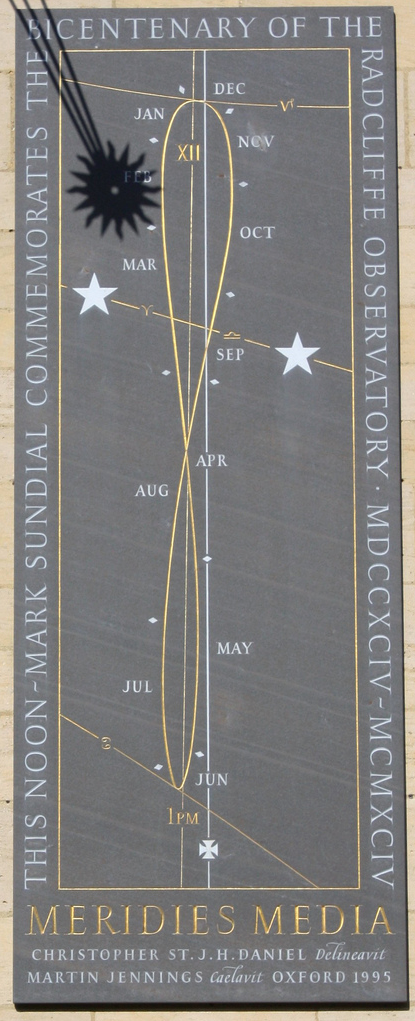

Christopher Daniel - 1995 - Radcliffe Observatory, Oxford, UK
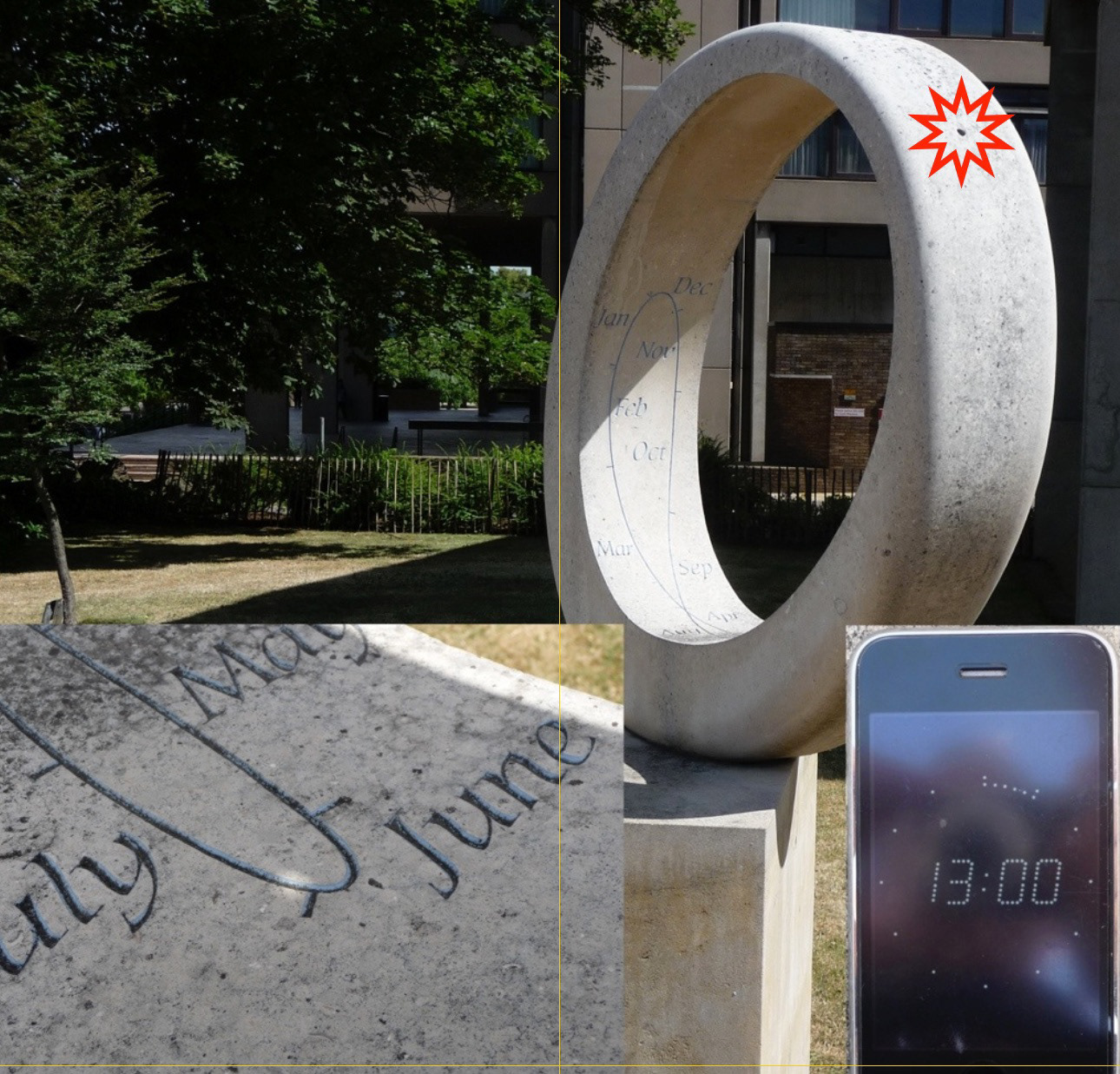

Dr Alan Mills - 2007 - Eye of Time, Leicester University, UK
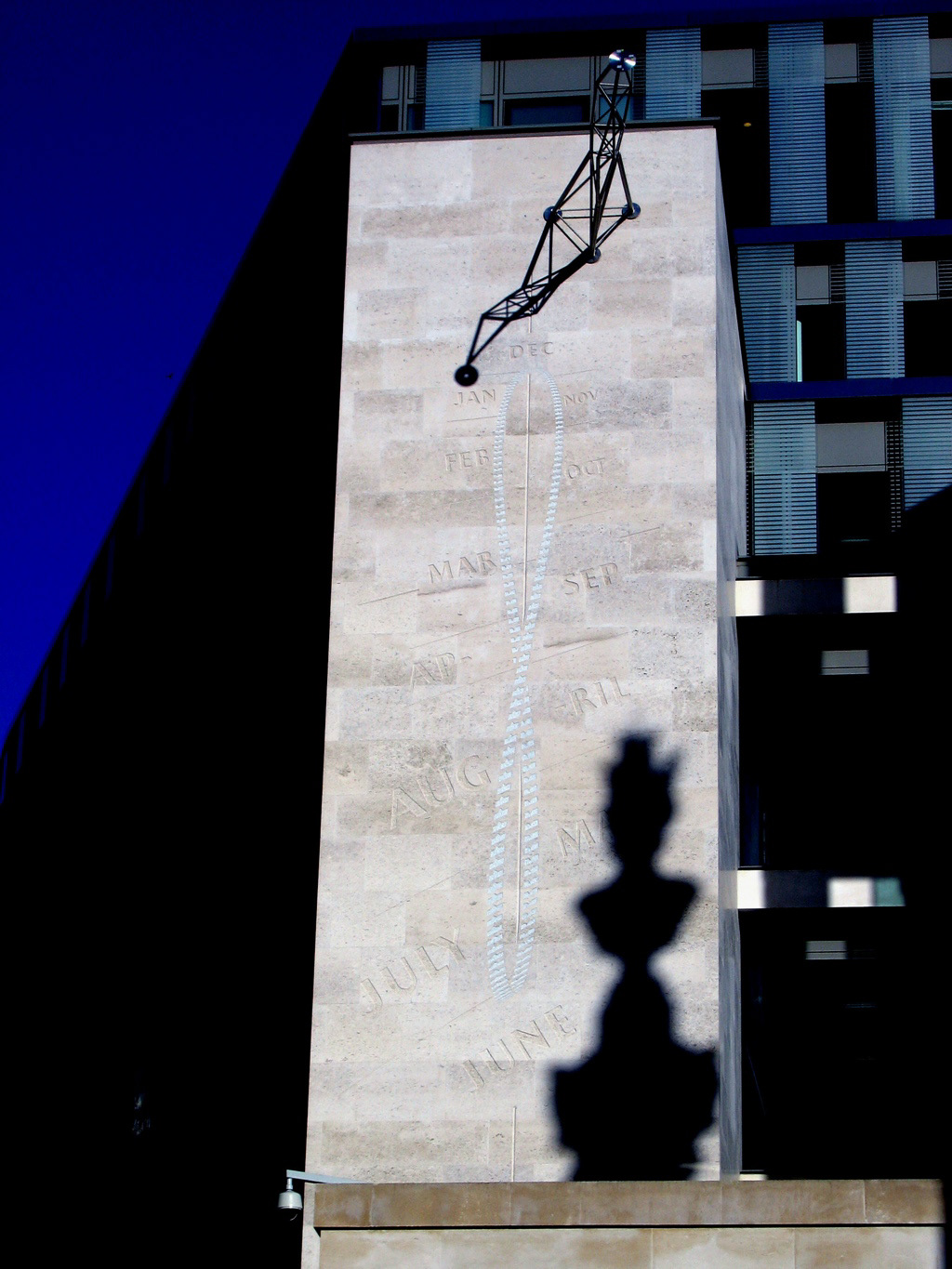

Dr Frank King - 2004 - London Stock Exchange, UK
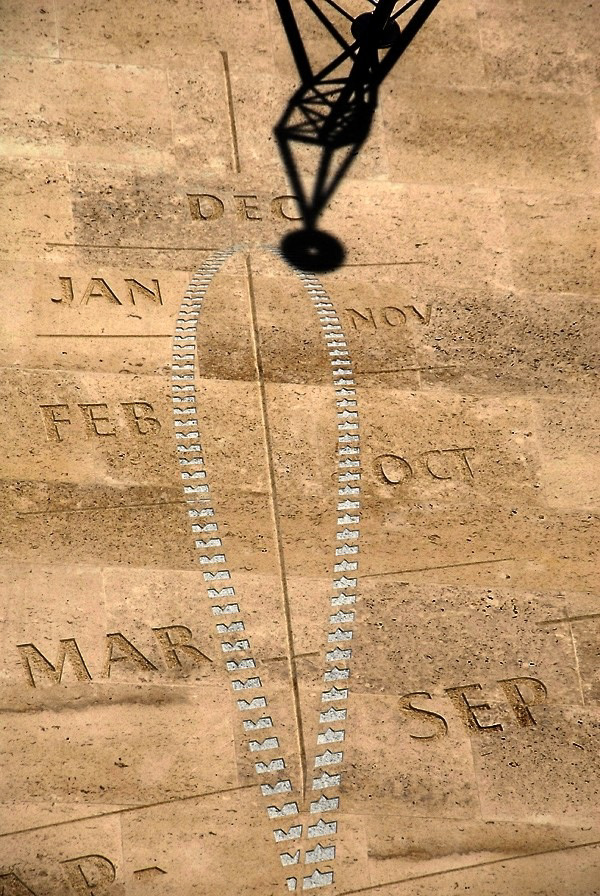

Detail from Stock Exchange Dial

Alastair Hunter - macmillanhunter.co.uk - 2011 - Noon Mark
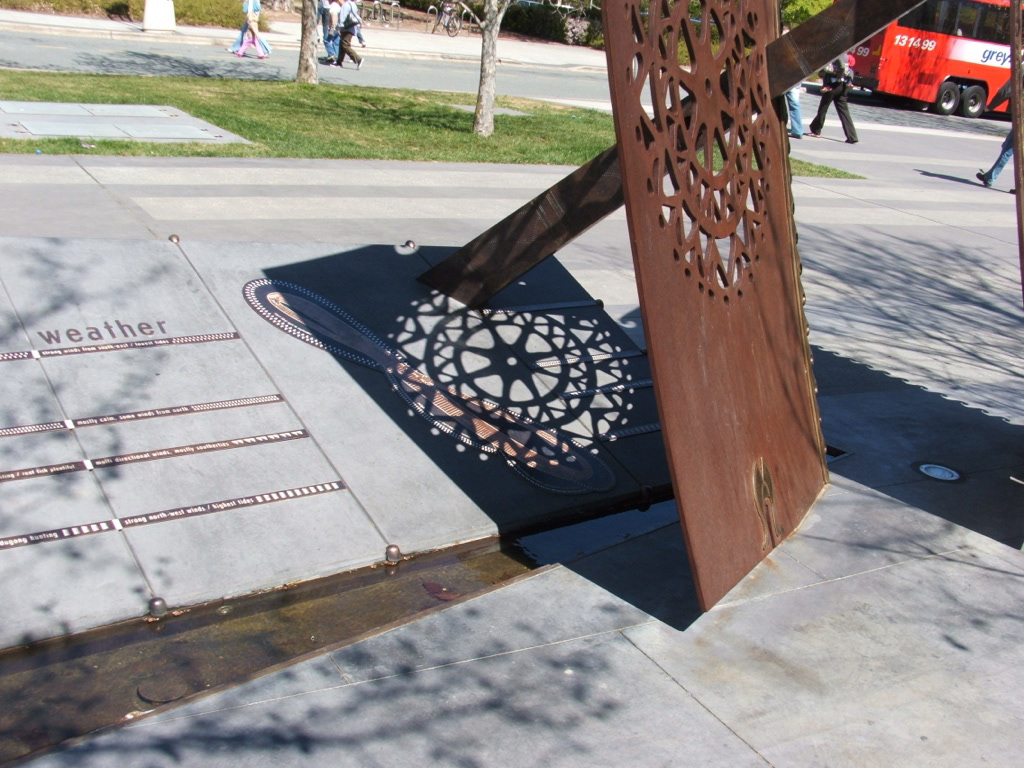

Vic McGrath - after 2001 - Smooth Sailing, Reconciliation Place, Canberra, Australia
Click on images to enlarge & view captions
SPIDER DIALS
These require a lot more calculation to delineate, but are used with a standard gnomon. A nice feature of the spider dial is its ability to indicate sunrise and sunset times
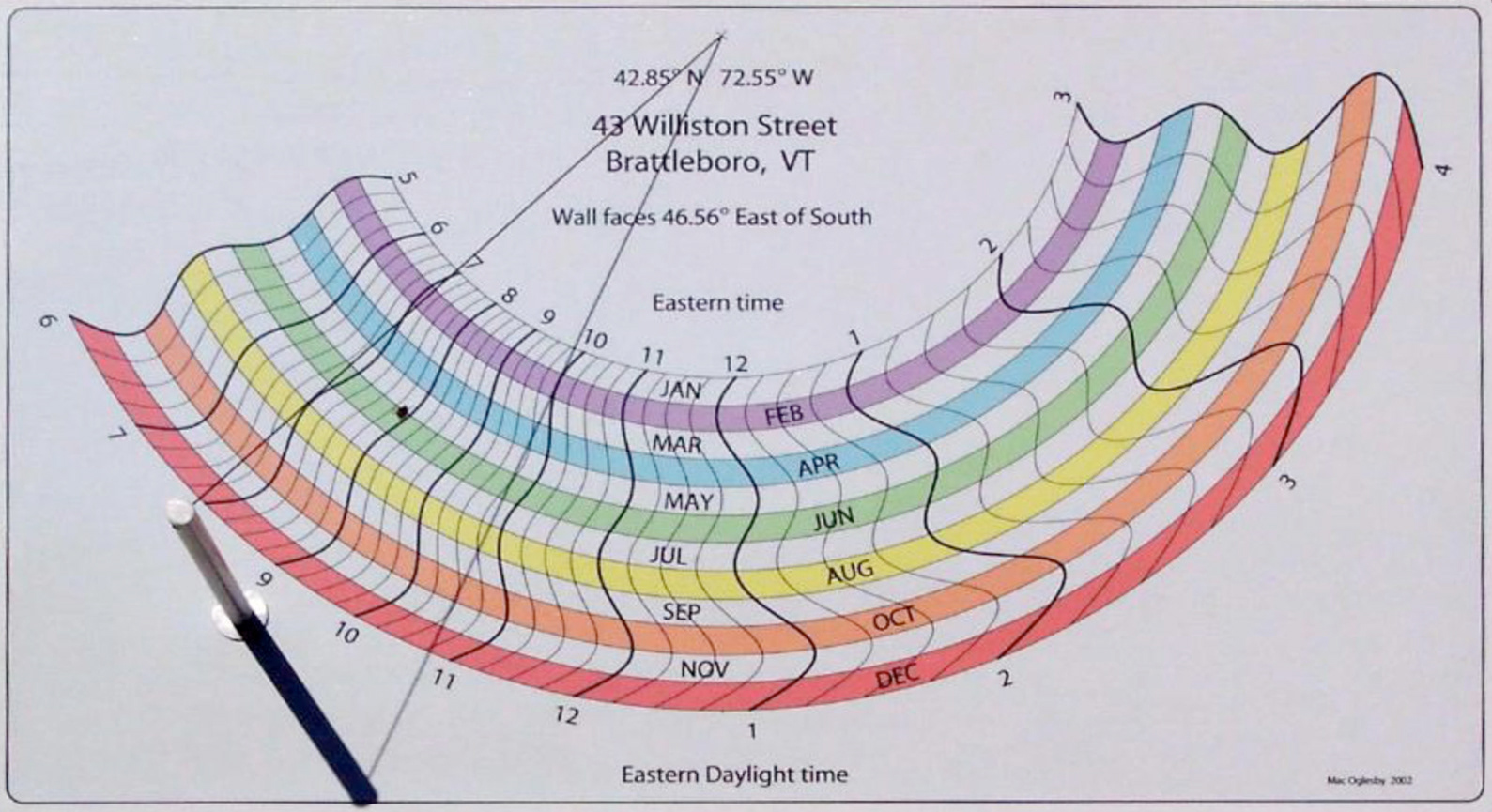
Mac Oglesby - 2002 - Vertical Declining "Rainbow" Spider Dial, Brattlesbury, Vermont, USA
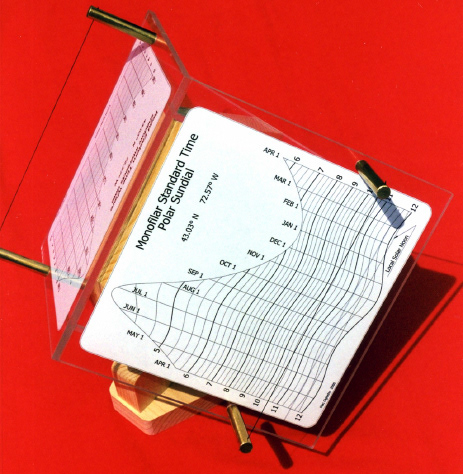
Mac Oglesby - Monofilar Standard Time Polar Dial

Rick Twardy - 2001 - Parkes Observatory, Dubbo, New South Wales

Author's bronze Highfield House dial - 2016 - before being exposed to the atmosphere
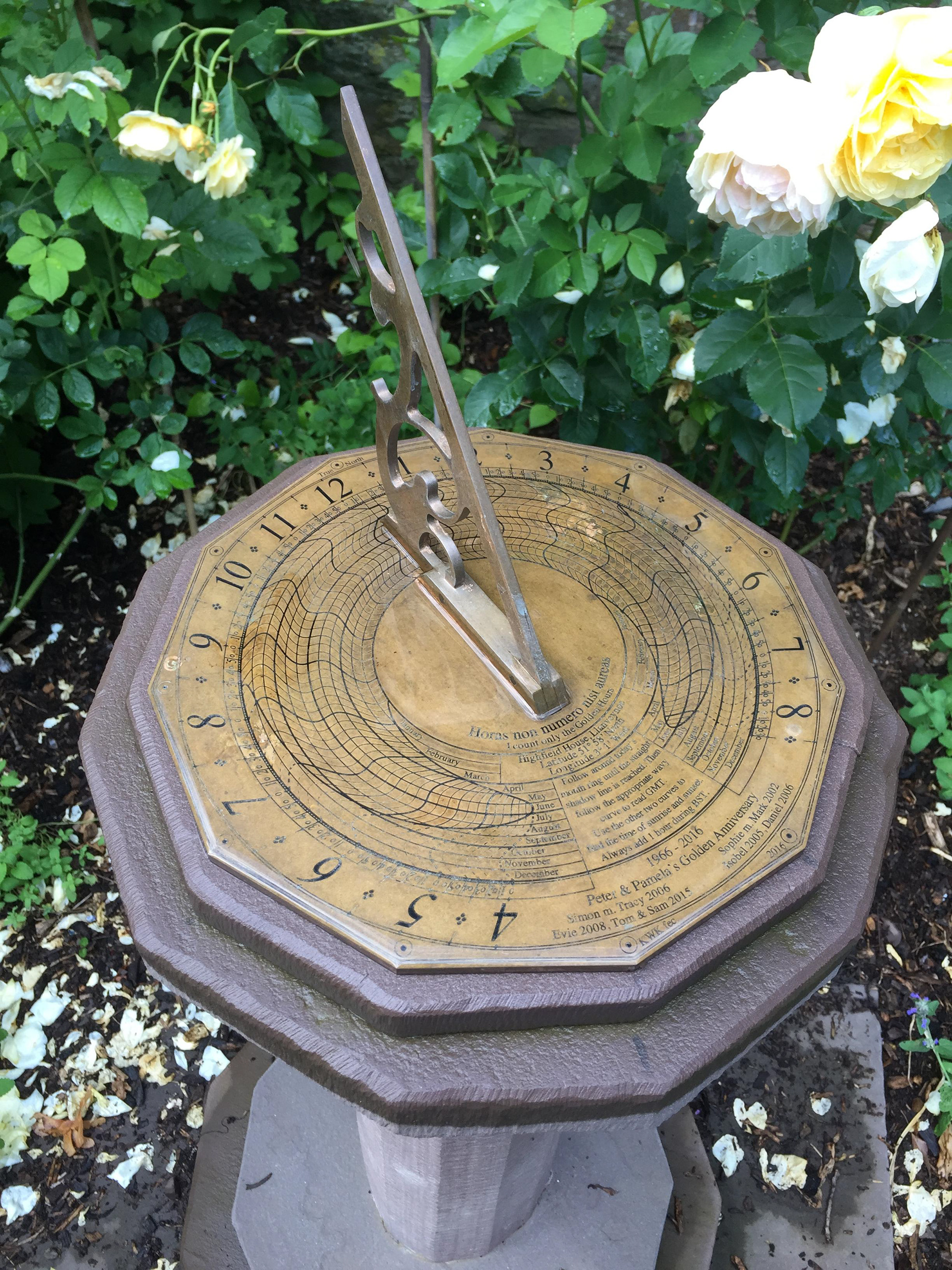

Highfield Dial after tow years in the atmosphere
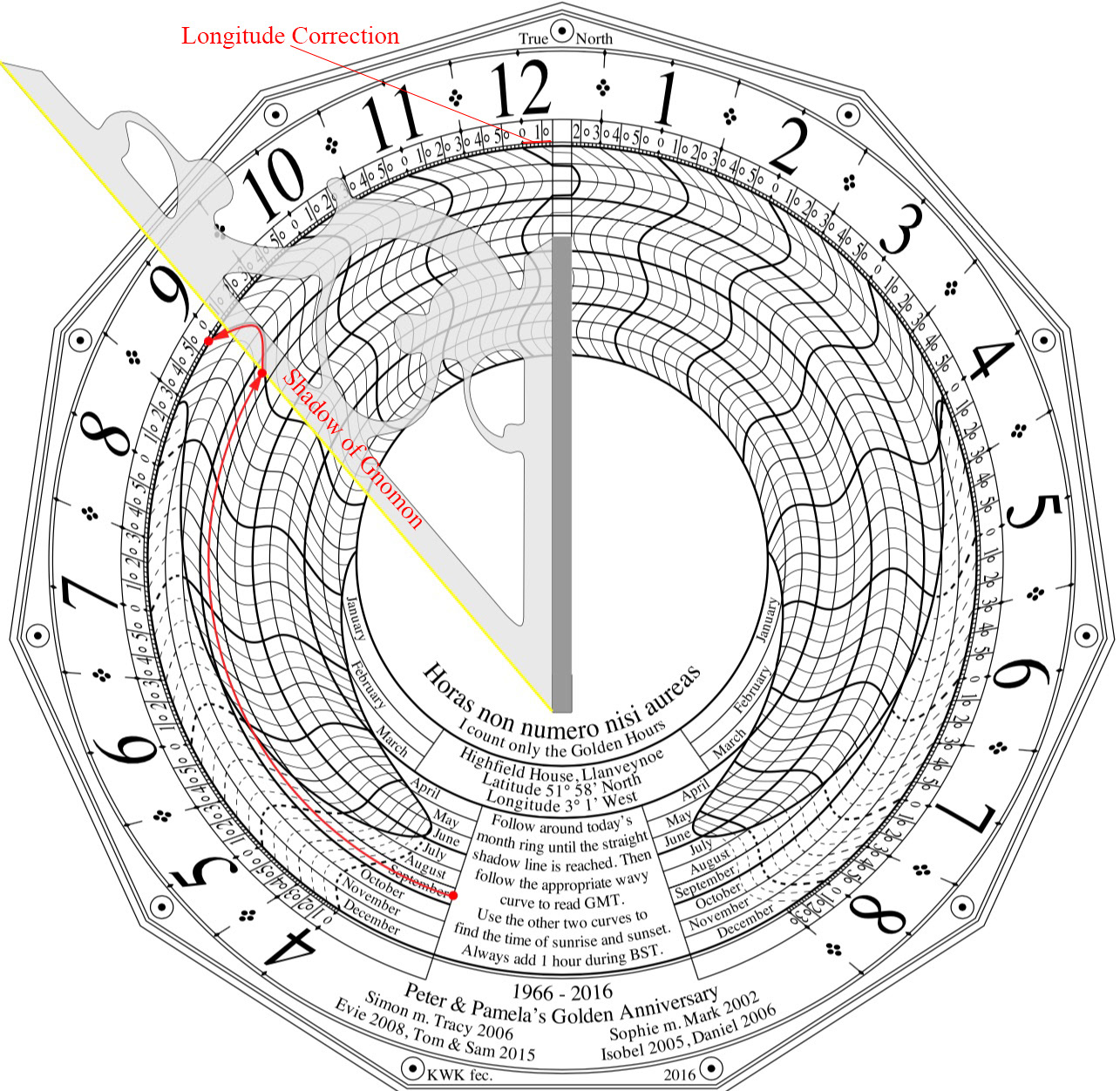
How to read a Spider dial.
Click on images to enlarge & view captions